Durable Siding Options A Guide to Long-Lasting Exteriors
Durable Siding Options are crucial for protecting your home and enhancing its curb appeal. Choosing the right siding isn’t just about aesthetics; it’s a long-term investment impacting durability, maintenance, and even your home’s resale value. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the various options available, helping you navigate the complexities of material selection, installation, cost, and long-term care. We’ll explore the pros and cons of popular siding choices, from classic wood to modern engineered alternatives, empowering you to make an informed decision that perfectly suits your needs and budget.
From understanding the nuances of vinyl’s affordability to the superior weather resistance of fiber cement, we’ll break down the key characteristics of each material. We’ll also address practical considerations like installation processes, maintenance requirements, and the environmental impact of your choice. Ultimately, our goal is to equip you with the knowledge necessary to select the perfect durable siding that not only protects your home but also reflects your personal style and enhances its value for years to come.
Types of Durable Siding
Choosing the right siding for your home is a significant investment, impacting both its curb appeal and long-term value. The durability and aesthetic qualities of your siding directly influence your home’s protection from the elements and its overall visual impact. Understanding the various options available is crucial for making an informed decision. This exploration will delve into the specifics of popular siding materials, outlining their advantages, disadvantages, and approximate costs.
Durable Siding Material Comparison
Selecting the ideal siding hinges on a variety of factors, including budget, aesthetic preferences, and climate. The following table provides a comprehensive overview of common siding materials, highlighting their respective pros, cons, and cost ranges. Remember that prices can fluctuate based on location, installer, and specific product features.
| Material | Pros | Cons | Cost Range (per sq ft) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | Affordable, low maintenance, wide variety of colors and styles, easy installation | Can fade or crack over time, less durable than other options, can dent easily | $2-$6 |
| Fiber Cement | Durable, fire-resistant, resists pests and rot, low maintenance, realistic wood-like appearance | More expensive than vinyl, requires professional installation, can be heavy and difficult to handle | $7-$15 |
| Wood | Beautiful natural aesthetic, can be painted or stained, relatively easy to repair | High maintenance, susceptible to rot, insect damage, and fire, requires regular painting or staining | $8-$20+ |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, durable, low maintenance, fire-resistant, resistant to insect damage | Can dent easily, susceptible to scratches, limited color options, can be noisy in rain or hail | $6-$12 |
| Engineered Wood | Durable, resistant to rot and insects, low maintenance, aesthetically pleasing | More expensive than vinyl, requires professional installation, can be susceptible to moisture damage if not properly installed | $9-$18 |
Lifespan and Maintenance of Siding Materials, Durable Siding Options
The longevity and maintenance requirements of your siding significantly impact its overall cost-effectiveness. Understanding these aspects is crucial for long-term planning and budgeting. For example, while vinyl siding boasts low maintenance, it may require replacement sooner than more durable options like fiber cement. Regular cleaning and occasional repairs are essential for maintaining the appearance and structural integrity of any siding material, regardless of its inherent durability.
Ignoring maintenance can lead to premature deterioration and costly repairs.
Check what professionals state about Top Siding Brands In The Uk and its benefits for the industry.
Aesthetic Considerations for Siding Materials
The visual appeal of your siding is a significant factor in your home’s overall aesthetic. Vinyl offers a wide range of colors and styles, mimicking the look of wood or stone at a lower cost. However, fiber cement siding provides a more authentic wood-grain texture and can be painted for greater customization. Wood siding offers unmatched natural beauty, but requires more maintenance to retain its aesthetic appeal.
Aluminum siding provides a sleek, modern look, while engineered wood offers a blend of durability and natural aesthetic. The best choice depends entirely on your personal preferences and architectural style. Consider the overall design of your home and surrounding landscape when making your selection. For instance, a rustic farmhouse might benefit from the warmth of wood siding, while a modern home might be better suited to the clean lines of aluminum.
Installation and Cost Considerations
Choosing the right siding isn’t just about aesthetics; the installation process and overall cost significantly impact your project’s success. Understanding these factors empowers you to make informed decisions and avoid costly surprises down the line. This section dives into the practicalities of siding installation and provides a realistic cost analysis, helping you budget effectively.
Siding installation is a multifaceted process, varying considerably depending on the chosen material. While DIY is possible for some types, professional installation often guarantees a longer-lasting, more aesthetically pleasing result, and avoids potential warranty issues. Factors like the complexity of the house’s design, existing siding removal, and necessary repairs also influence the overall time and labor involved.
Siding Installation Processes
The installation process differs based on the siding material. Vinyl siding, for example, involves interlocking panels that are nailed directly onto the sheathing. This requires basic carpentry skills and tools like a measuring tape, level, nail gun, and utility knife. Fiber cement siding, on the other hand, is more complex, often requiring specialized tools and more precise cuts due to its rigidity.
It necessitates more experience and potentially professional installation to ensure a seamless finish and avoid costly mistakes. Wood siding, a more traditional option, demands advanced carpentry skills and knowledge of proper sealing and treatment to prevent rot and insect infestation. Proper preparation of the underlying structure is critical for all siding types to ensure a long-lasting, secure installation.
Improper installation can lead to issues such as water damage, drafts, and premature deterioration.
Cost Breakdown Per Square Foot
The cost of siding installation varies widely depending on the material selected. As a general guideline, vinyl siding is often the most budget-friendly, ranging from $3 to $12 per square foot including materials and labor. Fiber cement, known for its durability, typically falls within the $8 to $20 per square foot range. Wood siding, with its aesthetic appeal, commands a higher price, often costing between $15 and $30 per square foot or more, depending on the type of wood and finish.
These figures represent averages and can fluctuate based on regional factors and the specifics of each project. For instance, a complex Victorian-style home will naturally cost more than a simple ranch-style house.
Factors Influencing Overall Cost
Several factors contribute to the total cost of siding installation beyond the material itself. A clear understanding of these elements allows for more accurate budgeting and avoids unforeseen expenses.
Understanding these variables is key to realistic budgeting. Ignoring these factors can lead to significant cost overruns.
- Project Size: Larger homes naturally require more materials and labor, increasing the overall cost.
- Location: Labor rates vary significantly by geographic location. Urban areas often have higher labor costs compared to rural areas.
- Labor Rates: The cost of labor is a significant component. Skilled installers command higher rates, reflecting their expertise and the quality of their work.
- Material Costs: Fluctuations in material prices due to supply and demand influence the overall cost. Choosing higher-end materials increases expenses.
- Existing Siding Removal: If you are replacing existing siding, the cost of removal adds to the total project expense. This is particularly true for older homes with multiple layers of siding.
- Complexity of the Project: Homes with intricate designs or multiple gables will require more time and labor, resulting in higher costs.
- Permits and Inspections: Building permits and inspections are necessary in most areas and contribute to the overall project cost.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Choosing the right siding for your home is a crucial decision, impacting not only its aesthetic appeal but also its longevity and resilience against the elements. Understanding the durability and weather resistance of different siding materials is paramount to making an informed choice that protects your investment for years to come. This section delves into how various siding options perform under pressure from wind, rain, snow, extreme temperatures, and other environmental stressors.
The performance of siding materials varies significantly depending on their composition and manufacturing process. Factors such as material density, water absorption rate, and the presence of protective coatings all contribute to a material’s overall durability and resistance to damage. Let’s examine how several popular siding choices measure up against these crucial factors.
Impact Resistance of Siding Materials
Impact resistance is a key consideration, particularly in areas prone to hailstorms or accidental impacts from falling debris. Materials like fiber cement and vinyl offer excellent resistance to dents and scratches, while wood siding, while aesthetically pleasing, is more susceptible to damage. Metal siding, such as aluminum or steel, boasts superior impact resistance, often exceeding that of other materials.
The thickness of the material also plays a crucial role; thicker siding generally provides greater protection against impact.
Moisture Resistance in Siding
Moisture penetration can lead to rot, mold growth, and structural damage. The ability of siding to repel water is therefore a critical factor in its longevity. Vinyl siding, with its inherently waterproof nature, excels in this area. Fiber cement siding, when properly sealed and installed, also provides excellent moisture resistance. Wood siding, however, is more vulnerable to moisture absorption, requiring regular maintenance and protective treatments to prevent damage.
Proper installation techniques, such as ensuring adequate flashing and drainage, are crucial regardless of the siding material chosen to mitigate moisture problems.
Insect and Pest Resistance of Exterior Cladding
Insect infestation can significantly compromise the structural integrity of your home’s exterior. Certain siding materials are more resistant to insect damage than others. Vinyl siding, for example, is generally impervious to insect infestation. Fiber cement siding, due to its composition, also offers good resistance. Wood siding, however, is susceptible to damage from termites, carpenter ants, and other wood-boring insects, requiring preventative treatments and regular inspections.
Metal siding is also naturally resistant to insect damage.
Comparison of Siding Durability
| Material | Impact Resistance | Moisture Resistance | Insect Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | Good | Excellent | Excellent |
| Fiber Cement | Excellent | Excellent | Good |
| Wood | Fair | Fair | Poor |
| Metal (Aluminum/Steel) | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
Maintenance and Repair
Proper siding maintenance is crucial for preserving its aesthetic appeal and extending its lifespan. Neglecting routine care can lead to costly repairs down the line, impacting both the home’s value and its energy efficiency. Regular inspections and prompt attention to minor issues can prevent significant damage and save you money in the long run. This section details the specific maintenance requirements for various siding types, offering practical guidance for addressing common problems.
Routine Maintenance for Different Siding Types
Different siding materials require unique care. Understanding these nuances is key to ensuring long-term performance. For instance, wood siding demands more frequent attention than vinyl, while fiber cement necessitates a different cleaning approach.
| Siding Type | Cleaning | Inspection | Repair |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | Regular washing with soap and water; power washing (low pressure) annually. | Visual inspection for cracks, dents, or discoloration at least twice a year. | Minor repairs often involve replacing damaged panels; significant damage may require professional help. |
| Wood | Regular cleaning with a mild detergent; staining and sealing every 2-3 years. | Thorough inspection for rot, insect damage, and cracks; check fasteners regularly. | Repairs can range from replacing damaged boards to extensive restoration; professional help is often necessary for significant damage. |
| Fiber Cement | Regular cleaning with soap and water; avoid harsh chemicals. | Inspect for cracks, chips, or loose panels annually; check for signs of moisture penetration. | Cracks and chips can often be repaired with patching compounds; larger damage usually requires panel replacement. |
| Metal | Regular cleaning with soap and water; occasional power washing (low pressure). | Inspect for dents, rust, or loose panels annually. | Dents can sometimes be repaired; rust requires immediate attention; panel replacement may be necessary. |
Addressing Common Siding Problems
Promptly addressing minor issues can prevent them from escalating into major, costly repairs. For example, a small crack left unattended can allow moisture to penetrate, leading to rot or mold.
Cracks
Step 1: Identify the crack’s location and extent.
Step 2: Clean the area thoroughly to remove dirt and debris.
Step 3: For minor cracks, use a suitable patching compound specifically designed for your siding type. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
Step 4: For larger cracks or significant damage, consider replacing the affected panel. This may require professional assistance.
Dents
Step 1: Assess the severity of the dent. Minor dents may require minimal intervention, while significant ones may necessitate panel replacement.
Step 2: For minor dents in vinyl or metal siding, carefully try to gently push the dent back into place. Use a soft object to avoid causing further damage.
Step 3: For significant dents, especially in wood or fiber cement, consider professional repair or panel replacement.
Discoloration
Step 1: Determine the cause of discoloration. This could be due to mildew, algae, or simply dirt buildup.
Step 2: Clean the affected area with a suitable cleaning solution, following the manufacturer’s recommendations for your siding type. For mildew or algae, a bleach solution (diluted appropriately) may be necessary. Always test in an inconspicuous area first.
Step 3: If discoloration persists after cleaning, consider repainting or restaining the siding, if appropriate for the material.
Replacement Parts and Repair Services
The availability and cost of replacement parts and repair services vary depending on the siding material and the extent of the damage. Vinyl siding parts are generally inexpensive and readily available at most home improvement stores. However, specialized parts for wood or fiber cement siding might require ordering from suppliers and may be more costly. Repair services range from DIY projects for minor repairs to professional assistance for extensive damage, with costs varying accordingly.
For example, replacing a single vinyl siding panel might cost under $50, including the material and labor if you do it yourself, whereas repairing extensive water damage to wood siding could run into thousands of dollars depending on the extent of the damage and the required professional services.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability: Durable Siding Options
Choosing durable siding isn’t just about aesthetics and longevity; it significantly impacts the environment. From manufacturing processes to eventual disposal, each siding material carries an ecological footprint. Understanding this footprint is crucial for making informed, sustainable choices for your home. This section explores the environmental impact of various siding materials, highlighting eco-friendly options and their energy efficiency.The manufacturing process of siding materials often involves energy-intensive steps and the use of raw materials with varying degrees of sustainability.
Disposal presents further challenges, with some materials contributing to landfill waste while others can be recycled or repurposed. The overall environmental impact is a complex interplay of these factors, influencing the long-term sustainability of your siding choice.
Manufacturing and Disposal Impacts of Different Siding Materials
Different siding materials have vastly different environmental impacts throughout their lifecycle. Vinyl siding, for example, is derived from petroleum, a non-renewable resource. Its manufacturing process consumes significant energy and releases greenhouse gases. Disposal can also be problematic, as vinyl doesn’t readily biodegrade and often ends up in landfills. Conversely, fiber cement siding, while requiring energy for manufacturing, uses readily available natural materials like cement and wood fibers.
While not completely environmentally benign, its disposal is less problematic than vinyl, as it can be crushed and used as aggregate in construction projects. Wood siding, a renewable resource, presents a more favorable environmental profile, particularly if sourced from sustainably managed forests. However, the treatment processes involved in protecting the wood from rot and insects can introduce chemical concerns.
Metal siding, often made from recycled aluminum or steel, boasts good recyclability, though its initial production requires substantial energy.
Environmentally Friendly Siding Options
Several siding options are gaining popularity due to their environmentally conscious attributes. Recycled materials find their way into some siding products. For example, some manufacturers incorporate recycled plastic into composite siding, diverting waste from landfills and reducing reliance on virgin materials. Bamboo siding, a rapidly renewable resource, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional wood siding, provided it’s sourced responsibly.
Similarly, responsibly harvested wood siding from certified sustainable forests minimizes environmental damage. The use of these materials contributes to a reduced carbon footprint and promotes the circular economy.
Energy Efficiency and Insulation Properties of Various Siding Types
The energy efficiency of your home is directly linked to your siding choice. Different siding materials offer varying levels of insulation, impacting heating and cooling costs.Choosing a siding with superior insulation properties can lead to significant energy savings over the lifetime of your home. This translates to lower utility bills and a smaller carbon footprint.
- Vinyl Siding: Offers minimal insulation; relies primarily on the underlying wall insulation for thermal performance.
- Fiber Cement Siding: Provides moderate insulation; its density helps to resist heat transfer.
- Wood Siding: Insulation properties vary greatly depending on the type and thickness of the wood; can be improved with proper installation and the addition of insulation beneath.
- Metal Siding: Generally offers low insulation; relies heavily on the building’s overall insulation system for energy efficiency. However, some metal sidings incorporate insulation backing.
- Composite Siding: Insulation properties vary depending on the composition; some composite sidings incorporate foam insulation for enhanced thermal performance.
Aesthetic Considerations and Design Options
Choosing the right siding not only protects your home but significantly impacts its curb appeal and overall aesthetic. The interplay of material, color, and style creates a unique visual identity, reflecting your personal taste and enhancing your property’s value. Careful consideration of these factors ensures a cohesive and visually stunning exterior.The selection of siding profoundly influences the character and style of a home.
Different materials offer distinct textures, appearances, and visual impacts, allowing for a wide range of design possibilities, from classic elegance to modern minimalism. Matching the siding to the architectural style is crucial for achieving a harmonious and aesthetically pleasing result.
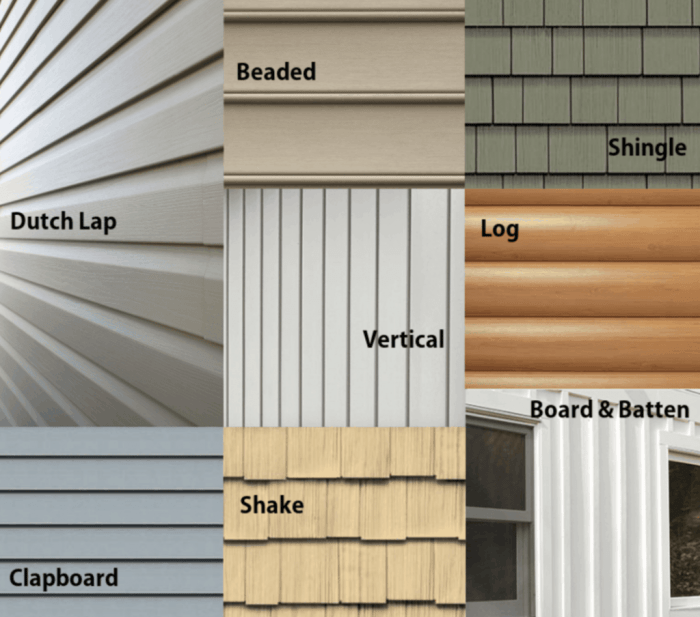
Siding Styles and Color Options
The availability of siding styles and colors is vast, offering homeowners extensive choices to personalize their homes. For instance, vinyl siding comes in a multitude of colors, mimicking the look of wood, stone, or brick. Fiber cement siding, known for its durability, provides a smooth or textured finish, offering a range of neutral and bolder color palettes. Wood siding, a classic choice, offers natural variations in color and grain, with options for staining or painting to further customize the look.
Metal siding, often used in contemporary designs, is available in various colors and finishes, including metallic shades.
Siding Materials and Architectural Styles
The successful integration of siding with architectural style enhances the home’s overall appeal. For example, a traditional colonial home might be complemented by clapboard siding, painted a classic white or a soft, muted tone. A Craftsman-style home might benefit from the natural textures and warm tones of wood siding, perhaps with a slightly weathered or aged appearance. Modern homes often incorporate sleek, clean lines, making metal or fiber cement siding a natural fit, often in a monochromatic color scheme.
A rustic farmhouse style could be beautifully accented with a rough-hewn wood siding or stone-like vinyl siding.
Siding Combinations and Patterns
Strategic combinations of siding materials and patterns can create striking visual effects and add depth to a home’s exterior. Imagine a home with a combination of dark gray fiber cement siding on the main structure, contrasted with lighter gray wood-style vinyl siding accents around windows and doors. This creates a visually interesting interplay of textures and tones. Another example might be a home with vertical wood siding on the upper story, transitioning to horizontal vinyl siding on the lower level, creating a sense of movement and visual interest.
A third option could utilize brick on the ground floor, transitioning to a light-colored stucco on the second floor, followed by a contrasting darker-colored metal roof. These layered approaches showcase the versatility of siding in achieving unique and sophisticated designs.
Conclusive Thoughts
Selecting durable siding is a multifaceted decision, balancing aesthetics, longevity, and budget. This guide has explored the diverse landscape of siding options, from the classic charm of wood to the modern efficiency of engineered materials. By weighing the pros and cons of each material – considering factors like weather resistance, maintenance needs, and environmental impact – you can confidently choose a siding solution that perfectly complements your home and lifestyle.
Remember, a well-informed decision ensures not only a beautiful exterior but also a long-lasting, protective shield for your most valuable asset.